
Serious Problem
Effective Solution
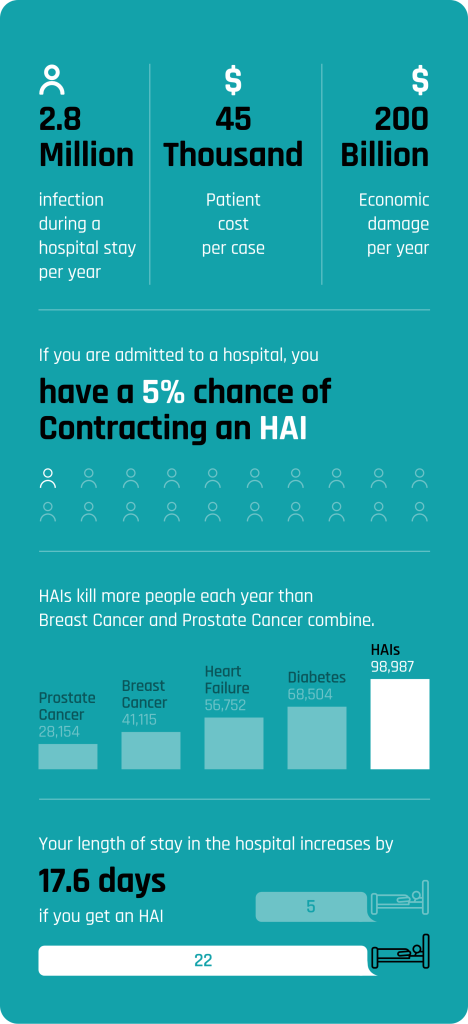
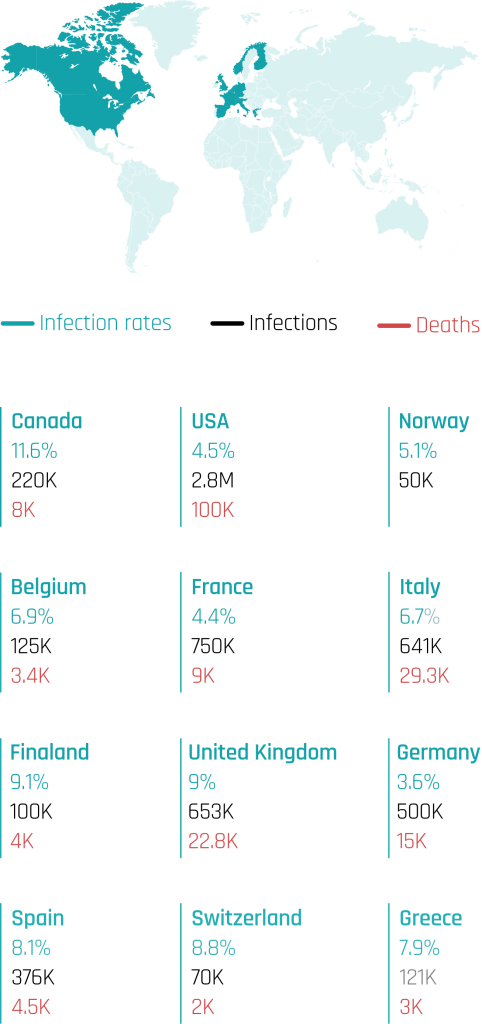
Hospital Acquired Infections are the most frequent adverse event in healthcare delivery worldwide, HAIs rate is 7.5% in high-income countries, while it varies between 5.7 and 19.2 in low-income countries percent . According to the WHO data, the HAIs rate is 25% in developing countries and 5–15% in developed countries. Eliminating bacteria is one of the most important sterilizing
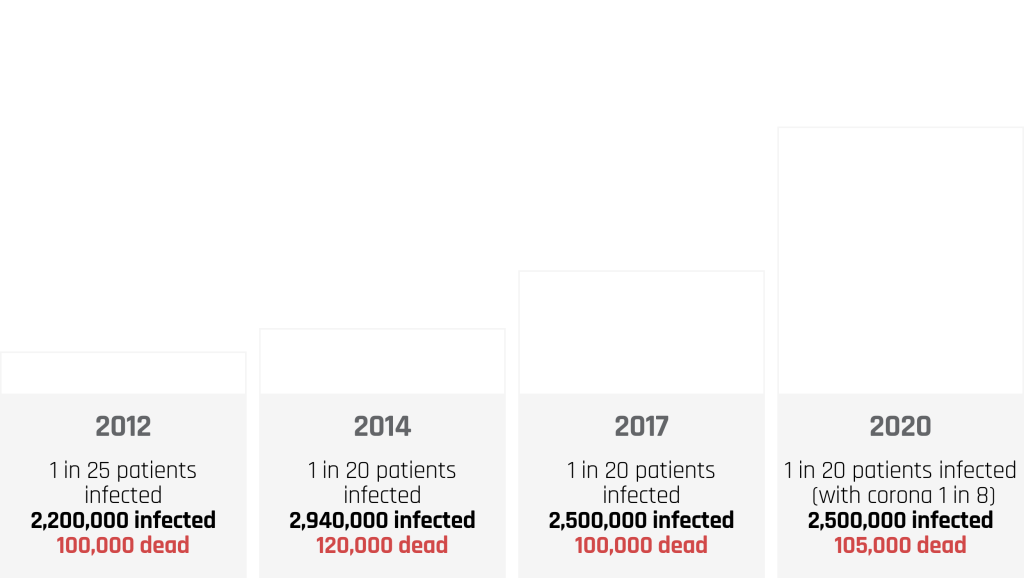
challenges hospitals face. Currently, in 2019 all over the world, in-hospital infections claim about 1.27 million lives a year, infect over 35 million people yearly. in two decades the world economic damage will be around 100 trillion dollars. (2023, World Health Organization.

The Role Of
Biofilms In HAIS
The Role Of Biofilms In HAIS
Biofilms are colonies of microorganisms that grow on living surfaces as well as non-living surfaces like medical devices. Responsible for an estimated 50% of all nosocomial infections, biofilms are particularly dangerous because they’ve demonstrated both immune system resistance and antimicrobial resistance. late studies show that biofilms develop resistance even to disinfectants.
“Once you have the biofilms in there, short of ripping the sinks and the piping out, it’s impossible to get rid of”



?What Is AMR
We are in an era of antimicrobial resistance. When bacteria don’t respond to antibiotic treatment methods, it becomes even more critical to protect vulnerable populations from encountering them.
But hospitals and researchers have not yet found a viable solution to the danger posed by biofilms in the plumbing. Clinical testing of a variety of disinfectants and cleaning methods have all come up short, and most preventative measures have met with failure or are prohibitive in cost and implementation.
Researchers have concluded that the solution lies in the design of the sink itself, making sure that the bacteria proliferating in the biofilm can not enter the hospital environment and endanger at-risk patients. That’s where capitalizing on natural physical laws has transformed the situation.
NeiMedica works in the sink itself, by not allowing contaminants back into the building.
Proven Effectiveness

The Economic
Damage Of HAI
The Economic Damage Of HAI

The Economic
Damage Of HAI
The Economic Damage Of HAI
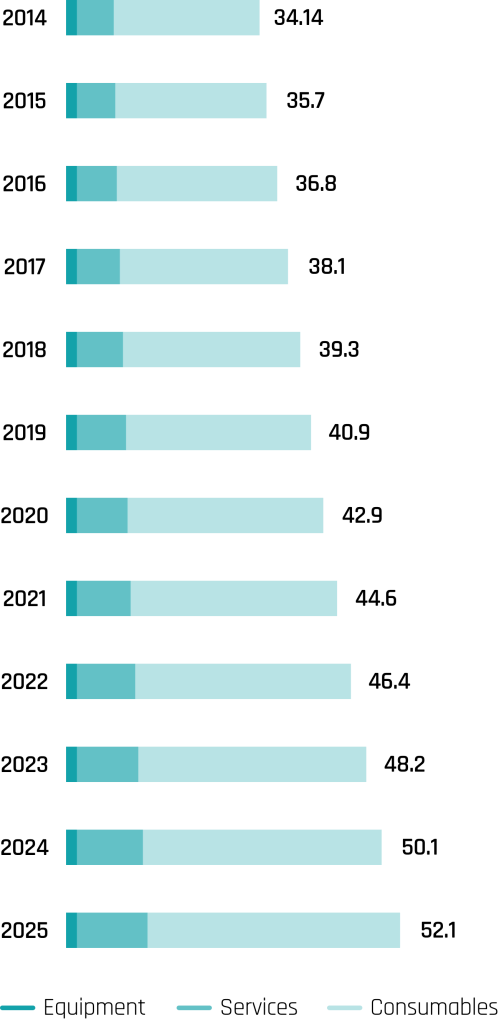
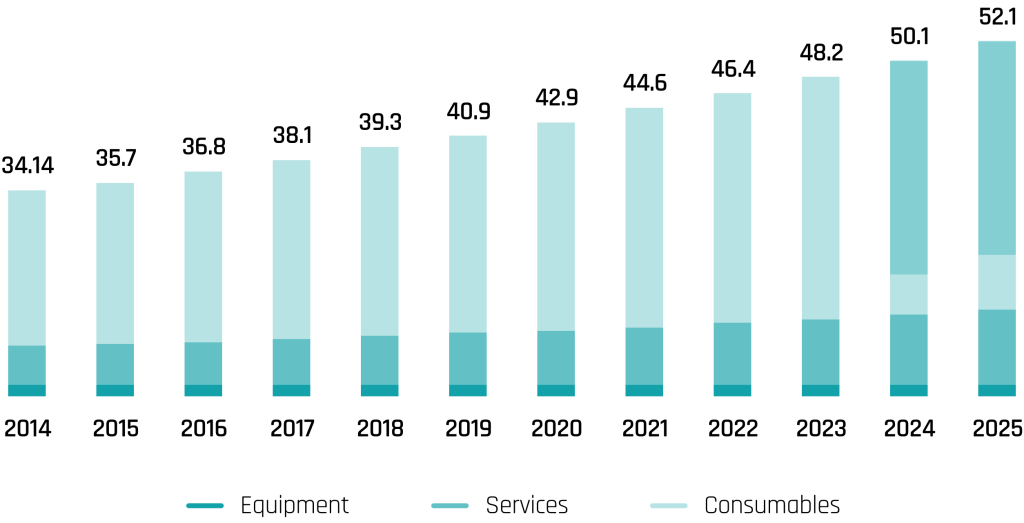
By type, 2014-2025 (USD Billion)
Economic Burden
Of HAI’s


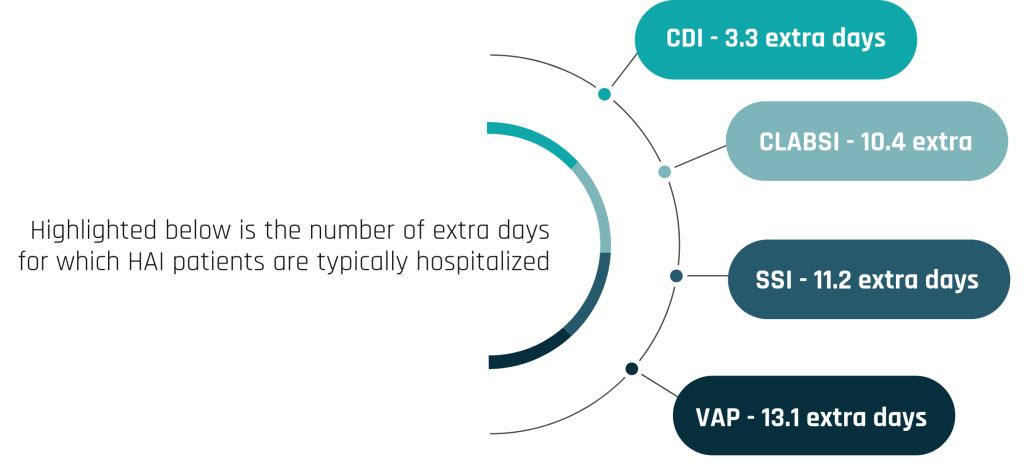

Our Solution
Our Products
Medical Siphon Basic
Simplicity is the name of the game. NEIMedica has developed a product that takes into account the needs of the field. NEIM edica product helps in significantly reducing infections while requiring minimal maintenance and at zero costs.


Medical Siphon Pro
The Medical Siphon ability to integrate is amazing, it is very easy to install, does not need any electricity source while utilizing water energy and simple laws of physics to protect the environment from a deadly enemy that destroys the lives of dozens of millions each year.
